AERATION
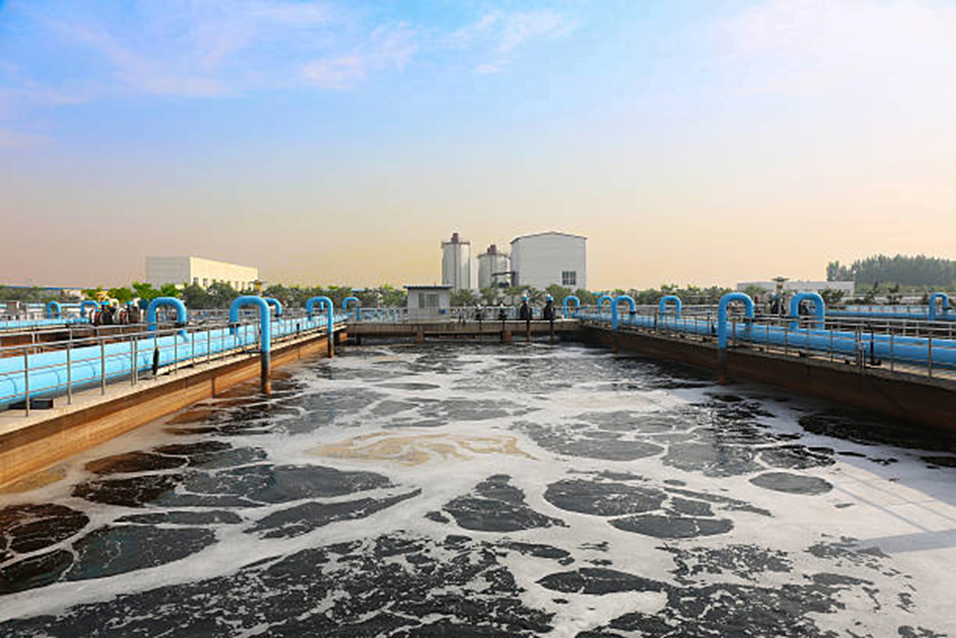

What is Aeration?
Aeration is the process by which air is circulated through, mixed with or dissolved in a liquid or other substances that act as a fluid.
Aeration meaning:
The introduction of air/ the process of adding air into wastewater
Aeration of water:
- Aeration of water is done to remove Dissolved gases such as hydrogen sulphide, methane, and radon are also eliminated by aeration.
- Although dissolved iron is oxidized by aeration, the resulting iron particles can foul the packing material in some aeration devices.
Need for Aeration:
- Aeration is a process that reduces the concentration of volatile organic compounds at the point of entry.
- Aeration is an important step in Sewage treatment for every industry to biologically treat the sewage for further treatments. It helps in reducing BOD.
Aeration tank:
- The biological treatment of the wastewater takes place in the aeration tank. Before the wastewater gets to this tank, it is mixed with activated sludge.
- This contains countless microorganisms, such as bacteria, that are able to break down the colloidal, organic contaminants dissolved in the wastewater.
Aeration in Wastewater Treatment
- In municipal and industrial wastewater treatment, aeration is part of the secondary treatment process.
- Aeration provides oxygen to bacteria for treating and stabilizing the wastewater.
- Oxygen is needed by the bacteria to allow biodegradation to occur.
- The supplied oxygen is utilized by bacteria in the wastewater to break down the organic matter containing carbon to form carbon dioxide and also water.
Wastewater Treatment Plant:
What is Wastewater Treatment Plant?
- Wastewater treatment is a process used to remove contaminants from wastewater and convert it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle.
- Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on the environment or is reused for various purposes. This process is called Water reclamation.
- The treatment process takes place in a Wastewater Treatment Plant.
Types of Wastewater Treatment Plant:
- The treatment plant used for treating domestic wastewater (municipal wastewater or sewage) is called a Sewage Treatment Plant.
- The treatment plant used for treating for industrial wastewater is called Effluent Treatment Plant
Sewage Treatment Plant:
- Sewage treatment (or domestic wastewater treatment, municipal wastewater treatment) is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable for discharge to the surrounding environment or an intended reuse application, thereby preventing water pollution from raw sewage discharges.
- Sewage contains wastewater from households and businesses and possibly pre-treated industrial wastewater.
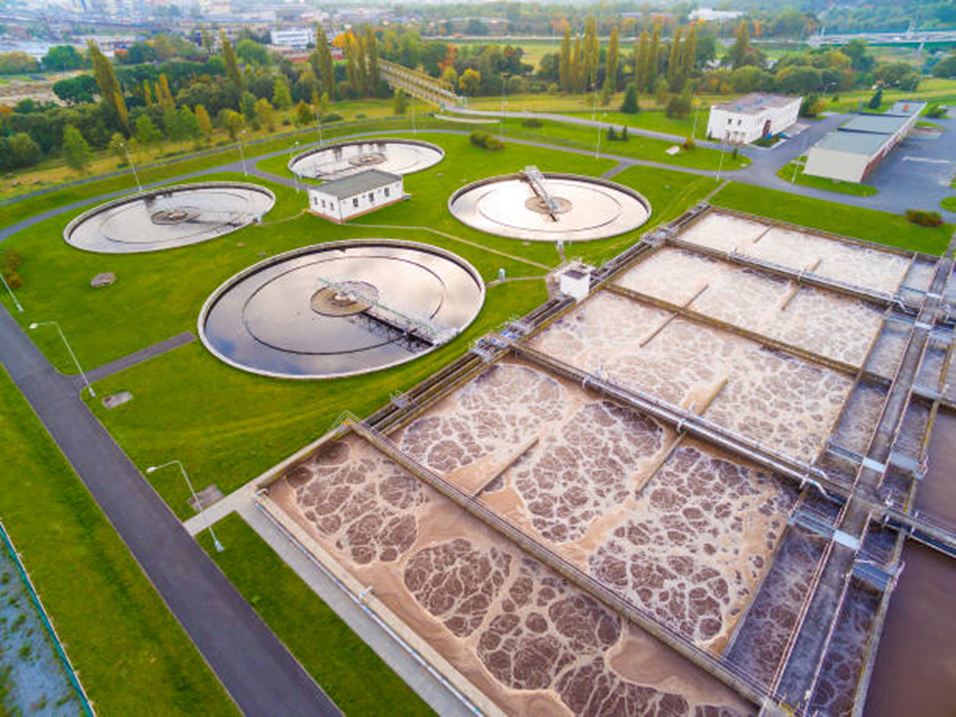

Sewage Treatment Plant Process:
- In a sewage treatment plant, sewage water is first allowed to pass through screens or grit chamber where large solids are removed.
- This step is followed by aeration/mixing in a tank and then primary sedimentation where suspended solids settle down.
Types of STP (Sewage Treatment Plant)
- Extended Aeration (E.A)
- Submerged Aeration Fixed Film (SAFF)
- Sequential Batch Reactor (SBR)
- Moving Bed Bio Reactor (MBBR)
- Membrane Bio Reactor (MBR)
Sewage Treatment Plant Diagram

Effluent Treatment Plant
ETP is one type of wastewater treatment method which is particularly designed to purify industrial wastewater for its reuse and its aim is to release safe water to environment from the harmful effect caused by the effluent.
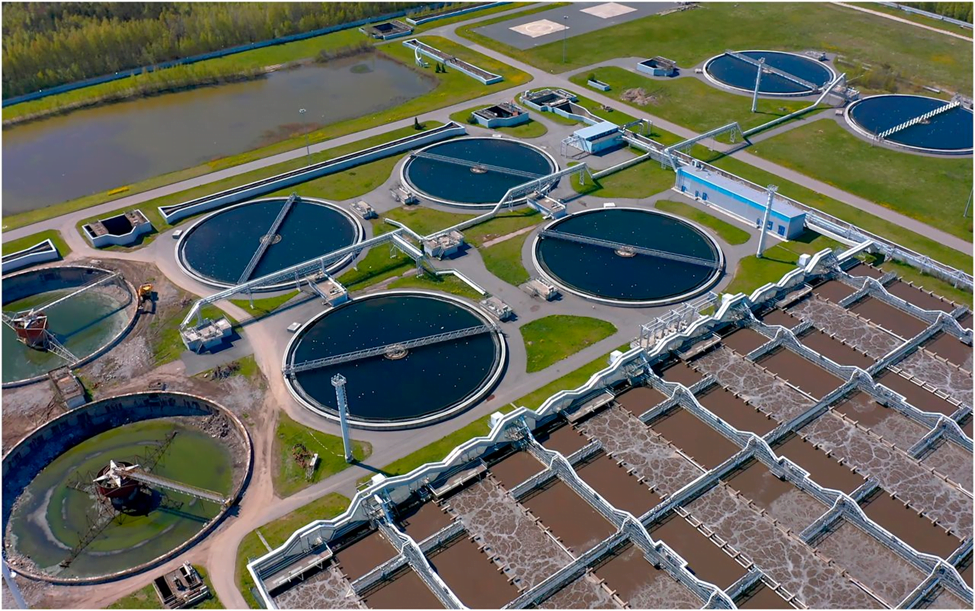

Effluent Treatment Plant Process
The treatment of different effluents varies with the type of effluent. Wastewater enters the effluent or sewage treatment plant and goes through several processes before effluent goes into the environment. Effluent treatment plant process includes the following stages:
STAGE 1: Preliminary Treatment: Its objective is physical separation of large sized contaminants. For example cloth, paper, plastics, wood logs etc. This level/process include:
- Screening
- Sedimentation
- Grit Chamber
STAGE 2: Primary Treatment: Its aim is removal of floating and settlable materials such as suspended solids and organic matter. In this treatment both physical and chemical methods are used. It includes:
- Flocculation
- Coagulation
- Neutralization
- Primary Clarifiers
STAGE 3: Secondary or Biological Treatment: The objective of this treatment is the further treatment of the effluent from primary treatment to remove the suspended solids and also residual organics. In this step biological and chemical processes are involved.
- Activated Sludge Process
- Aerated Lagoons
- Trickling Filters
- Rotating Biological Contactor
STAGE 4: Tertiary/advanced/disinfection treatment: The purpose of tertiary treatment is to provide a final treatment stage to raise the effluent quality to the desired level before it is reused, recycled or discharged to the environment.
- Chemical Coagulation and sedimentation.
- Filtration
- Reverse Osmosis
- UV Disinfection
Effluent Treatment Plant Diagram

Common effluent treatment plants (CETPs):
It is used for treating combined effluents generated from a cooperative group of small industries.
Common Effluent Treatment Plant process:

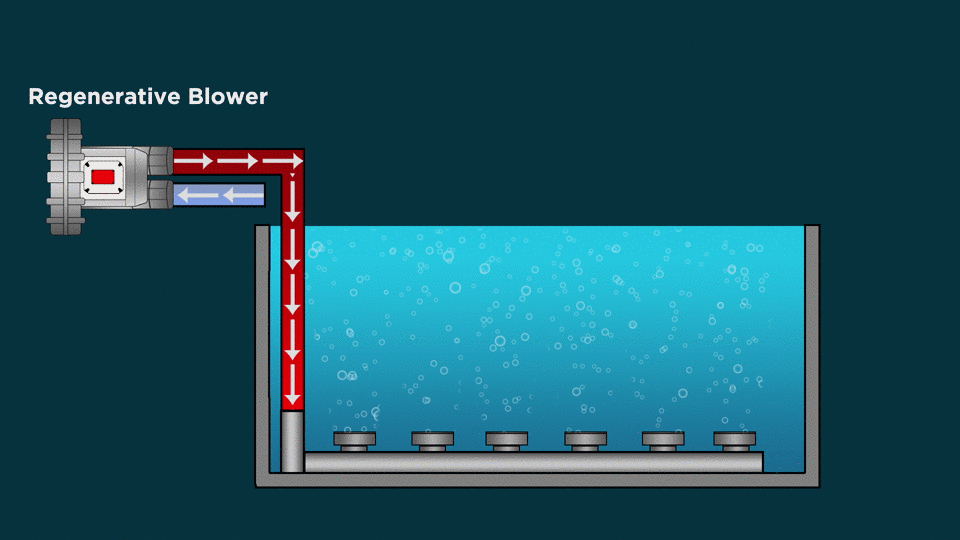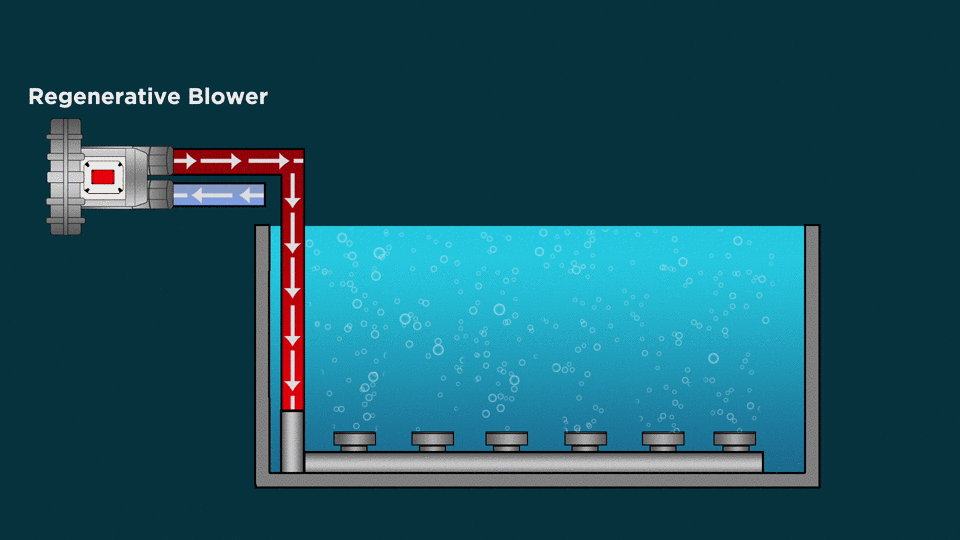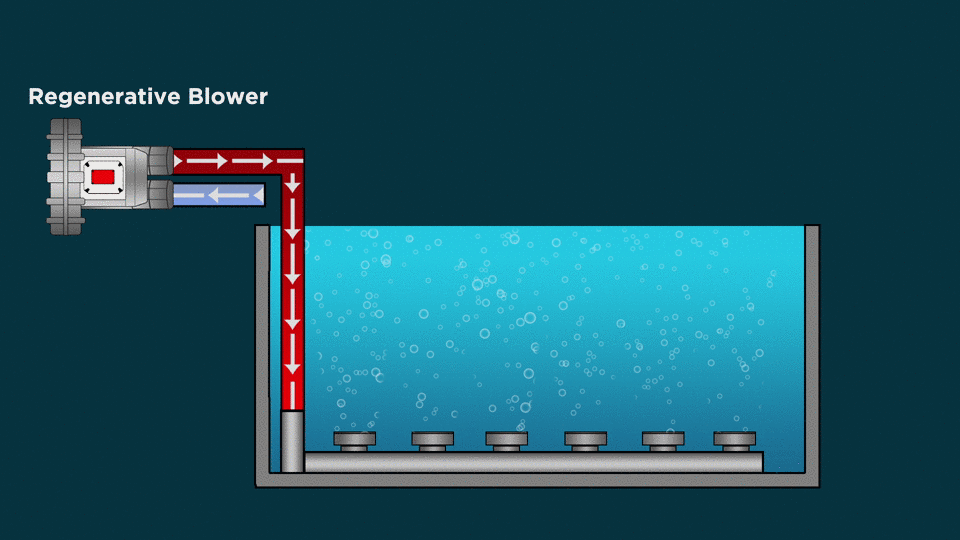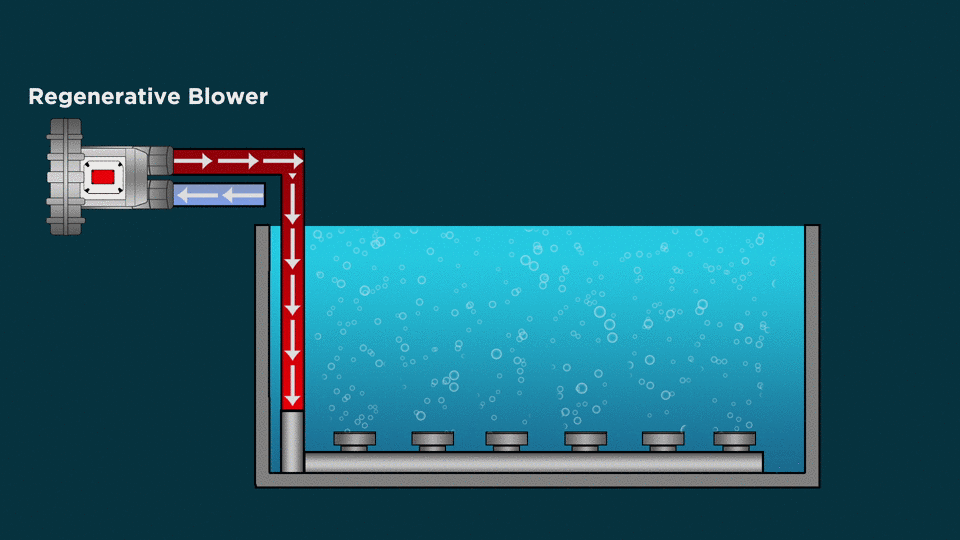
Types of Diffusion Aeration System:
Fine Bubble Diffusers

- Fine bubble diffusers are energy efficient submersible aeration systems for wastewater treatment.
- The fine bubble technology is a form of subsurface aeration that introduces air into water via very fine bubbles with the help of Diffusers. Thousands of the fine bubbles promote the transfer of oxygen to water, maximizing air-water contact in the process.
Coarse Bubble Diffusers
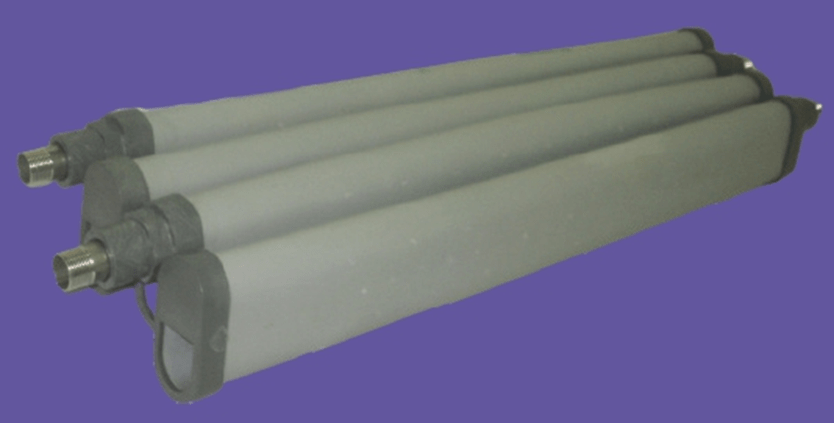

- Coarse bubble diffusers produce a larger diameter of bubble to displace, churn and mix the wastewater effectively.
Conclusion:
In both the STP & ETP Aeration is an Important process. Thus, selecting a High-quality Diffusers is critical for Trouble free operation of WTP.




3 Comments