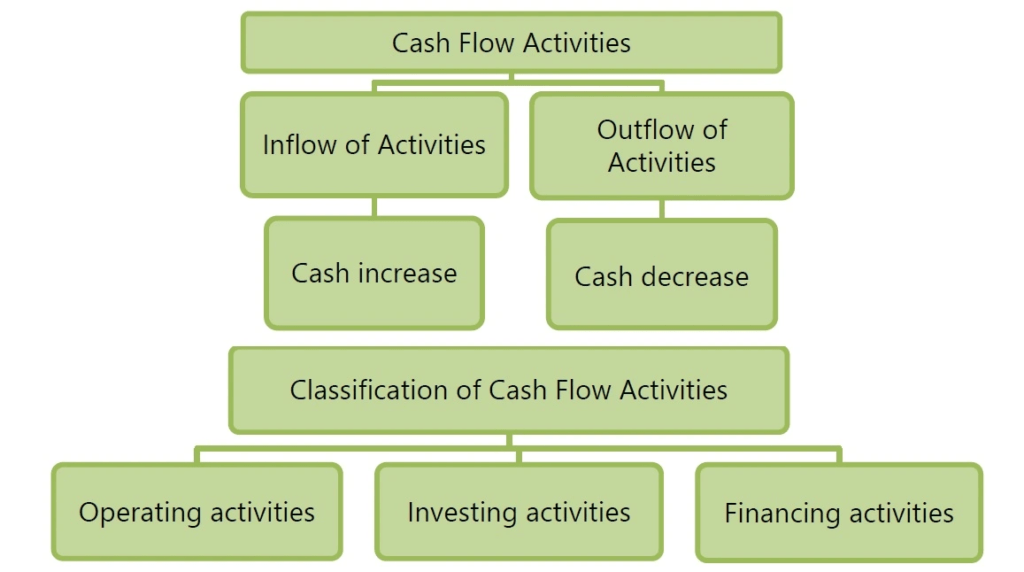
What are Cash Flow Statement
Cash flow statement is an important financial statement which shows inflows and outflows of the cash and cash equivalents. This statement is usually prepared by companies which comes as a tool in the hands of users of financial information to know about the sources and uses of cash and cash equivalents of an enterprise over a period of time from various activities of an enterprise.
Format of Cash Flow Statement
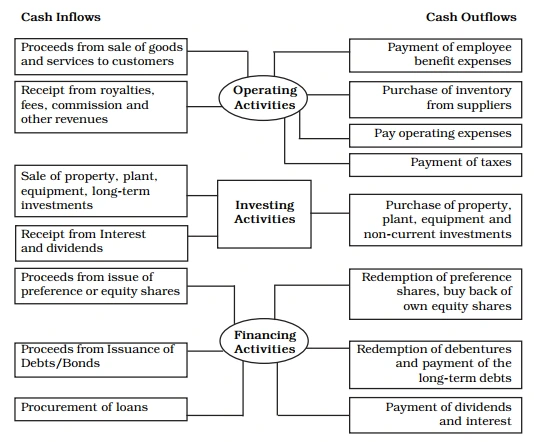
What is on Cash Flow Statement
- A Cash flow statement shows inflow and outflow of cash and cash equivalents from various activities of a company during a specific period. The primary objective of cash flow statement is to provide useful information about cash flows (inflows and outflows) of an enterprise during a particular period under various heads, i.e., operating activities, investing activities and financing activities.
- This information is useful in providing users of financial statements with a basis to assess the ability of the enterprise to generate cash and cash equivalents and the needs of the enterprise to utilise those cash flows. The economic decisions that are taken by users require an evaluation of the ability of an enterprise to generate cash and cash equivalents and the timing and certainty of their generation.
Cash Flows
Cash Flows meaning:
It implies movement of cash in and out due to some non-cash items. Receipt of cash from a non-cash item is termed as cash inflow while cash payment in respect of such items as cash outflow.
Cash Flows Operating Activities
Operating Activities include purchase of machinery by paying cash is cash outflow while sale proceeds received from sale of machinery is cash inflow. Other examples of cash flows include collection of cash from trade receivables, payment to trade payables, payment to employees, receipt of dividend, interest payments, etc
Importance of the Cash Flow Statement
Cash flow statement provides the following benefits :
- A cash flow statement when used along with other financial statements provides information that enables users to evaluate changes in net assets of an enterprise, its financial structure (including its liquidity and solvency) and its ability to affect the amounts and timings of cash flows in order to adapt to changing circumstances and opportunities.
- Cash flow information is useful in assessing the ability of the enterprise to generate cash and cash equivalents and enables users to develop models to assess and compare the present value of the future cash flows of different enterprises.
- It also enhances the comparability of the reporting of operating performance by different enterprises because it eliminates the effects of using different accounting treatments for the same transactions and events.
- It also helps in balancing its cash inflow and cash outflow, keeping in response to changing condition. It is also helpful in checking the accuracy of past assessments of future cash flows and in examining the relationship between profitability and net cash flow and impact of changing prices
How is Cash Flow Statement Prepared

According to Accounting Standard – 3 (Revised), following four steps are required:
- Calculation of Cash Flows from Operating Activities.
- Calculation of Cash Flow statement from Investing Activities.
- Calculation from Financing Activities.
- Calculation of net increase/decrease in cash and cash equivalents.
Calculation of Cash Flow from Operating activities
Cash flows from operating activities can be computed with the help of Income Statement of the current year, comparative Balance Sheets and the relevant additional information. As per AS – 3 (Revised), the following types activities can be regarded as cash flow from operating activities:
- Cash received from the sale of goods or rendering some services;
- Cash received from royalties, fees, commission and other revenue;
- Cash paid to suppliers for goods or services;
- Cash paid to employees or behalf of employees;
- Cash received or paid to insurance companies for premiums claims, annuities or other policy benefits;
- Cash paid as income tax or refund of income tax unless, they can be specifically identified with financing or investing activities; and
- Cash received or paid for future contracts, forward contracts, option contracts and swap contracts, when these are held for dealing or trading purpose.
Cash from Investing Activities
As per AS-3, investing activities are the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets and other investments not included in cash equivalents. Investing activities relate to purchase and sale of long-term assets or fixed assets such as machinery, furniture, land and building, etc. Transactions related to longterm investment are also investing activities. Separate disclosure of cash flows from investing activities is important because they represent the extent to which expenditures have been made for resources intended to generate future income and cash flows
Cash from Financing Activities
As the name suggests, financing activities relate to long-term funds or capital of an enterprise, e.g., cash proceeds from issue of equity shares, debentures, raising long-term bank loans, repayment of bank loan, etc. As per AS-3, financing activities are activities that result in changes in the size and composition of the owners’ capital (including preference share capital in case of a company) and borrowings of the enterprise.
Example For Cash Flow Statement
Let’s see the example for cash flow statement by two methods.
DIRECT METHOD
In this method figures of income statement, e.g., sales, purchases, stock expenses are so analyzed to convert income statement based on cash basis. In this method cash realized from sales and cash paid for purchases and expenses will be ascertained
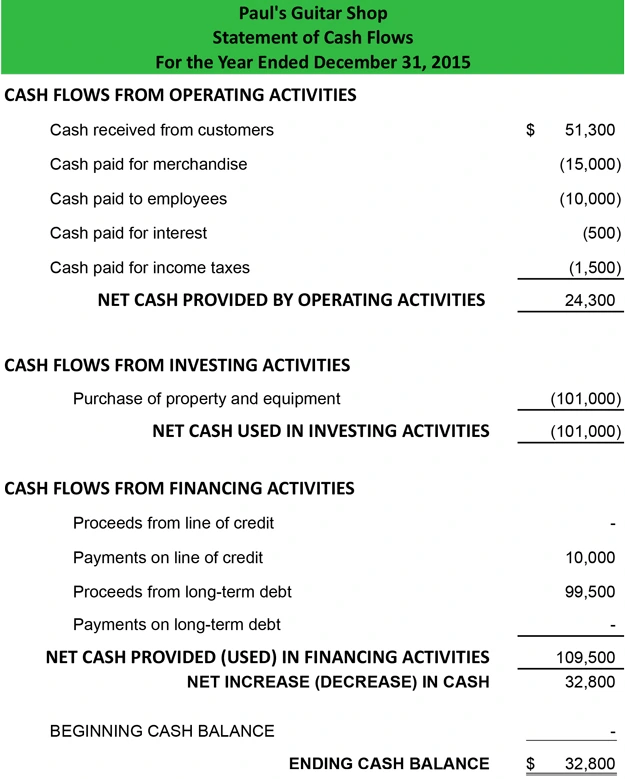
INDIRECT METHOD

For calculating from operating activities through indirect method, we start from the figure of profit, which should be before tax and extra-ordinary item. Further, this profit requires certain adjustments related to non-cash and non-operating items like:
- An increase or decrease in the value of current assets and current liabilities, which also affect the cash flows, so these should be adjusted to net profit.
- Loss on sale of assets, depreciation or fictitious or intangible assets written off are to be added back because they are non-cash items that do not result in the outflows of cash.
- Other items which effects investing or financing cash flows such as profit on sale of assets, dividend or interest income, etc.
LIKE WHAT YOU’RE READING?
CHECK OUT SOME OF OUR OTHER GREAT CONTENT HERE:
- WHAT IS ZERO-BASED BUDGETING
- CHARACTERISTICS OF THE MIXED ECONOMY
- UNDERSTANDING DIGITAL MARKETING
- IMPACT OF MARKETING ON SOCIETY
- PERFORMANCE MARKETING – A BEGINNER’S GUIDE
- EFFECTIVE BRANDING METHODS
- UNDERSTANDING CONSUMER BEHAVIOR
- HOW TO INCREASE SALES?
- HOW AI IS USED IN DIGITAL MARKETING?
- 5 BEST SOCIAL MEDIA PLATFORMS FOR BUSINESS IN 2022
- WHAT IS AFFILIATE MARKETING? (HOW TO GET STARTED)
- SWOT ANALYSIS WITH EXAMPLE
- WHAT IS THE DEFINITION OF ECOMMERCE



