
Methods of Starting a Synchronous Motor
A synchronous motor cannot start by itself. The following are various Synchronous Motor Starting Method:
- By using a pony motor (Small induction motor) (external prime mover)
- By using a damper winding
- By using DC motor
- Starting as an induction motor
- Finally, in some big installations the motor may be brought up to speed by a variable frequency electronic source
Must Read: WHY THE SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR IS NOT SELF STARTING
Synchronous Motor Starting Method
Basically, there are three methods that are used to start a synchronous motor:
- To reduce the speed of the rotating magnetic field of the stator to a low enough value that the rotor can easily accelerate and lock in with it during one half-cycle of the rotating magnetic field’s rotation. This is done by reducing the frequency of the applied electric power. This method is usually followed in the case of inverter-fed synchronous motor operating under variable speed drive applications.
- To use an external prime mover to accelerate the rotor of synchronous motor near to its synchronous speed and then supply the rotor as well as stator. Of course, care should be taken to ensure that the directions of rotation of the rotor as well as that of the rotating magnetic field of the stator are the same. This method is usually followed in the laboratory- the synchronous machine is started as a generator and is then connected to the supply mains by following the synchronization or paralleling procedure. Then the power supply to the prime mover is disconnected so that the synchronous machine will continue to operate as a motor.
- The damper windings are provided in most of the large synchronous motors in order to nullify the oscillations of the rotor whenever the synchronous machine is subjected to a periodically varying load. Each of these methods of starting a synchronous motor are described below in detail
Must Read: WORKING PRINCIPLE OF SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR
Synchronous Motor Starting Method by using a pony motor (Small induction motor):

- Very large synchronous motors (20 MW and more) are sometimes brought up to speed by an auxiliary motor, called a pony motor.
- It could be either 3 phase induction motor or DC shunt motor.
- In this method, the rotor of the synchronous motor is brought to its synchronous speed with the
- help of an external induction motor or DC motor.
- No DC excitation applied initially.
- It rotates at speed very close to its synchronous speed, and then we give the DC excitation.
- After some time when magnetic locking takes place supply to the external motor is cut off.
- Since the load is not connected to the synchronous motor before synchronizing, the starter motor has to overcome the inertia of synchronous motor at no load.
- The rating of the starter motor is much smaller than the rating of synchronous motor.
- At present most of the large synchronous motors are provided with brushless excitation system mounted on their shaft.
- These excitation systems are used as starting motor
Synchronous Motor Starting Method by using a Damper Winding:
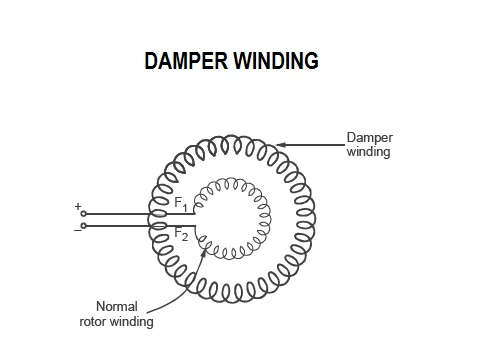
- The motor is equipped with a squirrel case winding, to start it as an induction motor.
- The damper windings are provided on the pole face slots in the fields of rotor.
- These windings are short-circuited at both ends with the help of end rings, thus forming a squirrel-cage system.
- When the synchronous motor is started as a slip-ring induction motor, the three ends of the windings are connected to an external resistance in series through slip-rings.
- Initially, when the rotor is not rotating, the relative speed between damper winding and rotating air gap flux is large and an emf is induced in it which produces the required starting torque.
- Now, when a three-phase supply is given to the stator of a synchronous motor, it will start as a three-phase induction motor.
- The motor accelerates until it reaches slightly below synchronous speed.
- As the motor approaches synchronous speed, the DC excitation is applied to the field windings.
- As speed approaches synchronous speed, emf and torque are reduced and finally when magnetic locking takes place; torque also reduces to zero.
- Hence in this case synchronous motor first runs as three phase induction motor using additional
- winding and finally it is synchronized with the frequency.
- It is the most widely used method of starting.
LIKE WHAT YOU’RE READING?
CHECK OUT SOME OF OUR OTHER GREAT CONTENT HERE:
- WHAT IS A UNIVERSAL MOTOR ?
- LVDT- CONSTRUCTION, WORKING PRINCIPLE , APPLICATIONS, ADVANTAGES, AND DISADVANTAGES
- HOW AN IGBT WORKS?
- SCR VI CHARACTERISTICS EXPLAINED IN DETAIL
- STEP UP TRANSFORMER: DEFINITION, CONSTRUCTION, WORKING & APPLICATIONS
- LIMITATIONS OF OHM’S LAW
- INDUCTION MOTOR: WORKING PRINCIPLE, TYPES & APPLICATION
- STRAIN GAUGE WORKING PRINCIPLE
- WHAT IS THE ZENER DIODE? – EXPLAINED
- WHAT IS OPERATING SYSTEM AND ITS TYPE
- WHAT ARE THE USES OF CAPACITOR
- CHARACTERISTICS OF A ZENER DIODE – EXPLAINED
- VOLTAGE REGULATION BY ZENER DIODE – EXPLAINED




9 Comments