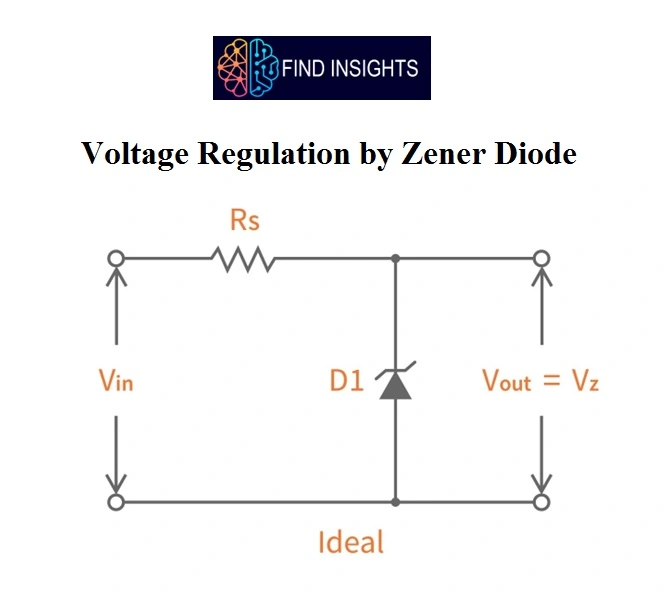
Voltage Regulation by Zener Diode
The Zener diode, with its accurate and specific reverse breakdown voltage, allows for a simple, inexpensive voltage regulator. Lets see in detail about Voltage Regulation by Zener diode.
With an ideal Zener diode, construction of a voltage regulator is easy, simply connect the diode between the unregulated voltage and ground. Since the exploited property of Zener diodes is the reverse breakdown voltage, connect the anode of the diode to ground, not the cathode.
Voltage regulation with Zener Diode
- Keeping the zener diode in parallel with a variable load resistance RL, ensures a constant output voltage even though the load current and the supply voltage varies. In practical circuits the simplest form of current source is a resistor.
- The key in using the Zener Diode as voltage regulator is that as long as the Zener Diode is reverse biased, the flow of current greater than a few micro amperes must be accompanied by a voltage greater than the Zener voltage.
- This type of arrangement of the circuit provides safety for equipment connected to terminals. This arrangement of regulator circuit is referred to as a shunt regulator in which the regulating element is placed in parallel with the load.
Working Principle – Voltage Regulation by Zener Diode
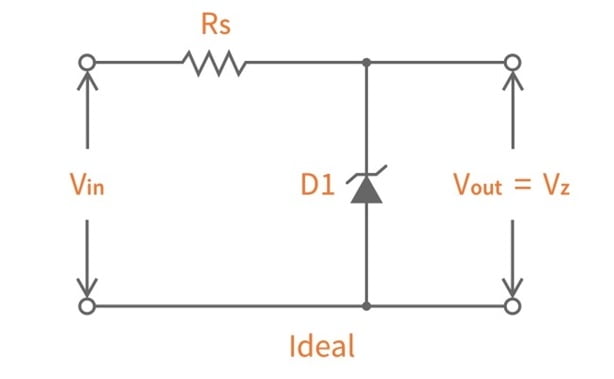
- Zener Diodes can be used to produce a stabilized voltage output with low ripple under varying load current conditions. By passing a small current through the diode from a voltage source, via a suitable current limiting resistor (RS), the zener diode will conduct sufficient current to maintain a voltage drop of Vout.
- DC output voltage from the half or full-wave rectifiers contains ripple superimposed onto the DC voltage and that as the load value changes so to does the average output voltage.
- By connecting a simple Zener stabilizer circuit as shown below across the output of the rectifier, a more stable output voltage can be produced.
LIKE WHAT YOU’RE READING?
CHECK OUT SOME OF OUR OTHER GREAT CONTENT HERE:
- LVDT- CONSTRUCTION, WORKING PRINCIPLE , APPLICATIONS, ADVANTAGES, AND DISADVANTAGES
- HOW AN IGBT WORKS?
- SCR VI CHARACTERISTICS EXPLAINED IN DETAIL
- STEP UP TRANSFORMER: DEFINITION, CONSTRUCTION, WORKING & APPLICATIONS
- LIMITATIONS OF OHM’S LAW
- INDUCTION MOTOR: WORKING PRINCIPLE, TYPES & APPLICATION
- STRAIN GAUGE WORKING PRINCIPLE
- TYPES OF LIGHTNING ARRESTER
- WHAT IS OPERATING SYSTEM AND ITS TYPE
- WHAT ARE THE USES OF CAPACITOR
- POWER FACTOR IMPROVEMENT METHODS
- WORKING PRINCIPLE OF SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR
- SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR STARTING METHOD
- WHY THE SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR IS NOT SELF STARTING



10 Comments