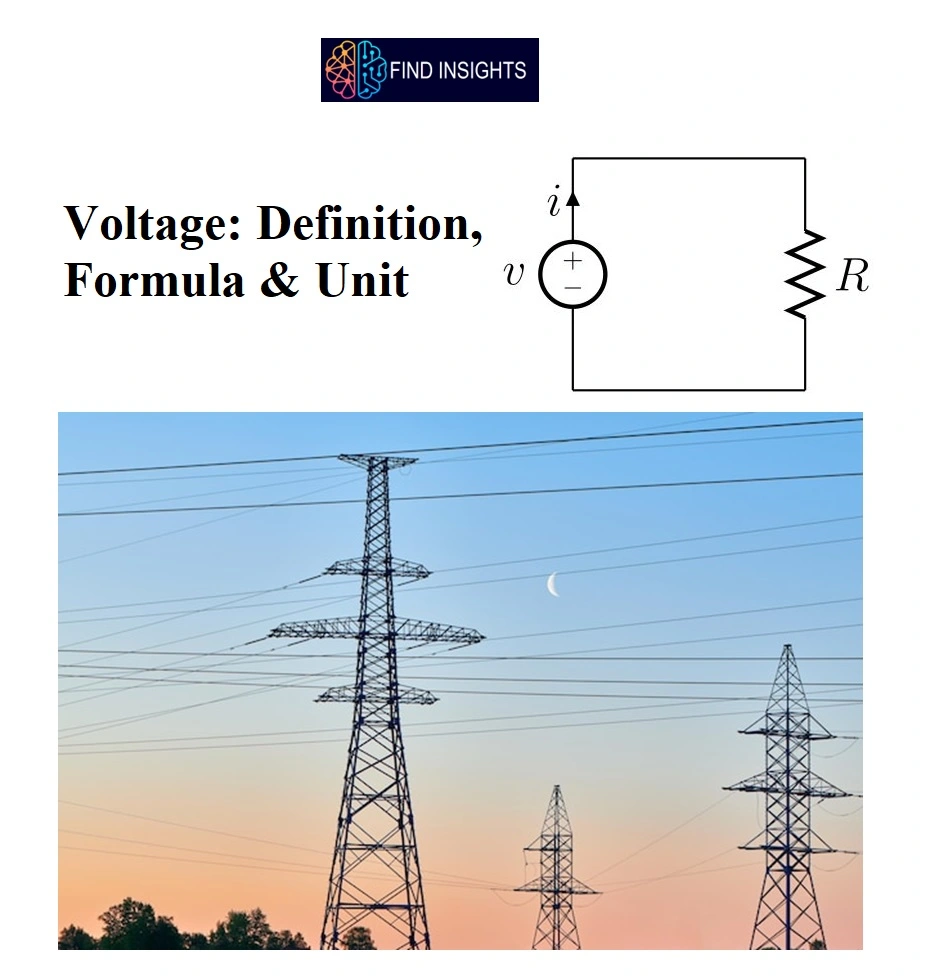
Voltage is the electrical force that would drive an electric current between two points. Voltage is caused by potential difference between two points. Let’s see Voltage Definition, formula of voltage & Voltage Unit
Voltage Definition
Voltage (or potential difference) is defined as the energy required to move a unit charge through an element, measured in volts (V). In other words Voltage is the difference in electrical potential energy of a unit of charge moved between two locations in an electrical field.
To move the electron in a conductor in a particular direction requires some work or energy transfer.
This work is performed by an external electromotive force (emf), typically represented by the battery. This emf is also known as Voltage or Potential difference. The voltage Vab between two points a and b in an electric circuit is the energy (or work) needed to move a unit charge from a to b; mathematically,
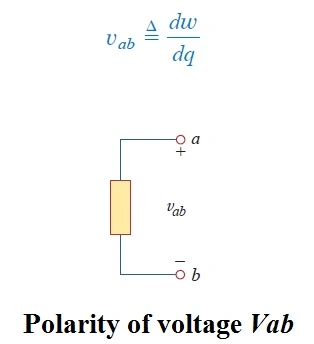
Where W is energy in joules (J) and q is charge in coulombs (C). shows the voltage across an element (represented by a rectangular block) connected to points a and b. The plus (+) and minus (-) signs are used to define reference direction or voltage polarity. The Vab can be interpreted in two ways:
- Ppoint a is at a potential of vab volts higher than point b, or
- The potential at point a with respect to point b is Vab. It follows logically that in general.
Vab = – Vba
Properties of Voltage
- Voltage is always measured as a difference
- Follows Ohm’s Law
Voltage Unit:
Voltage or simply Vis measured in volts (V), named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Antonio Volta (1745–1827), who invented the first voltaic battery.
1 Volt = 1 Joule/Coulomb = 1 Newton-Meter/Coulomb
Formula of Voltage
As per Ohm’s law Formula of Voltage is given by,
V = IR
In Ohm’s rule, V is the voltage measured in volts, I is the current measured in amperes, and R is the Resistance measured in ohms
Measurement of Voltage:
- Voltmeter measures DC and AC voltage
- Oscilloscope measures voltage changes as function of time (Vv/st)
Measuring Voltage: Voltmeters
Voltage is measured using Voltmeter. To measure potential-difference, or voltage, a voltmeter must be connected between two points at different potentials. In other words, a voltmeter must always be connected in parallel with the part of the circuit under test
LIKE WHAT YOU’RE READING?
CHECK OUT SOME OF OUR OTHER GREAT CONTENT HERE:
- WORKING OF AN INDUCTOR – EXPLAINED
- STEP UP TRANSFORMER: DEFINITION, CONSTRUCTION, WORKING & APPLICATIONS
- LIMITATIONS OF OHM’S LAW
- WHAT ARE THE USES OF CAPACITOR
- VARIOUS USES OF A RESISTOR
- DEFINITION FOR ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT
- DEFINITION & FORMULA OF POWER IN ELECTRICAL
- FORMULA FOR ELECTRICAL CURRENT – EXPLAINED
- WHAT IS THE ZENER DIODE? – EXPLAINED
- CHARACTERISTICS OF A ZENER DIODE – EXPLAINED
- VOLTAGE REGULATION BY ZENER DIODE – EXPLAINED



22 Comments