How the MOSFET works: Operation of a MOSFET, MOSFET Types: Enhanced and Depletion MOSFET
Introduction: How the MOSFET works
Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistors commonly known as MOSFETs are electronic devices used to switch or amplify voltages in circuits. It is a voltage controlled device and is constructed by three terminals. Lets see How the MOSFET works: Operation of a MOSFET, MOSFET Types: Enhanced and Depletion MOSFET in detail.
What is MOSFET Transistor?
- MOSFET is a voltage controlled field effect transistor that differs from a JFET in that it has a “Metal Oxide” Gate electrode which is electrically insulated from the main semiconductor n-channel or p-channel by a very thin layer of insulating material usually silicon dioxide, commonly known as glass.
- As the Gate terminal is electrically isolated from the main current carrying channel between the drain and source, “NO current flows into the gate” and just like the JFET, the MOSFET also acts like a voltage controlled resistor where the current flowing through the main channel between the Drain and Source is proportional to the input voltage.
Differences Between BJT and MOSFET
- BJT’s are used for low current applications, whereas MOSFET is used for high power applications. The metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) is used in a variety of applications similar to the BJT.
- Due to its unique features and areas of application, the MOSFET has become by far the most widely used electronic device, especially in the design of integrated circuits (ICs), which are entire circuits fabricated on a single silicon chip.
- Compared to BJTs, MOSFETs require very small area on the silicon IC chip, simpler manufacturing process and also requires comparatively little power. Furthermore, it has also been possible to implement digital and analog functions utilizing MOSFETs with essentially no (or very low) diodes or resistors required. These unique properties have led to the revolution of the semiconductor industry.
MOSFET Types
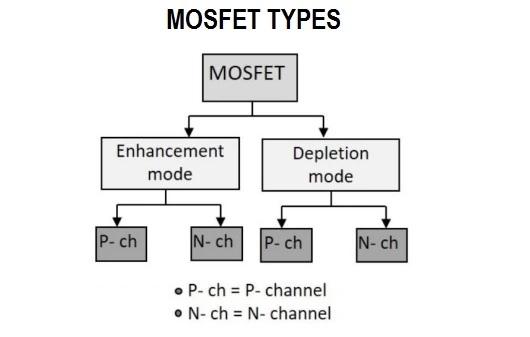
Depending upon the type of materials used in the construction, and also the type of operation, the MOSFET types are classified as below. MOSFETs are of two classes: Enhancement mode and depletion mode. Each class is available as n-channel or p-channel; hence overall they tally up to four types of MOSFETs.
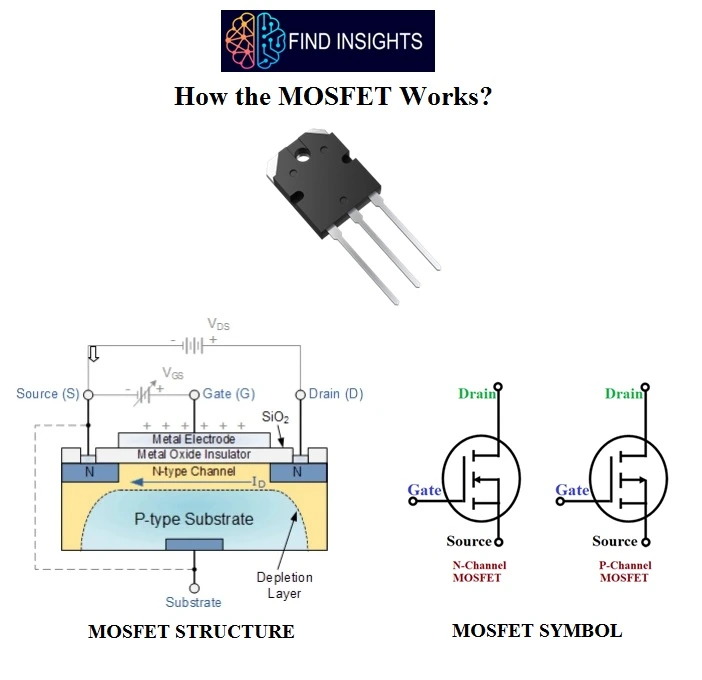
MOSFET N Channel and P Channel
A type of MOSFET in which the MOSFET channel is composed of a majority of charge carriers as current carriers like electrons is known as N channel MOSFET.
The P channel MOSFET has a P- Channel region located in between the source and drain terminals. P-Channel MOSFETs use hole flow as the charge carrier, which has less mobility than electron flow.
Enhanced and Depletion MOSFET
Both the p-channel and the n-channel MOSFETs are available in two basic forms, the Enhancement type and the Depletion type.
Operation of a MOSFET
Let’s see the Operation of MOSFET with basic structure
Basic MOSFET Structure
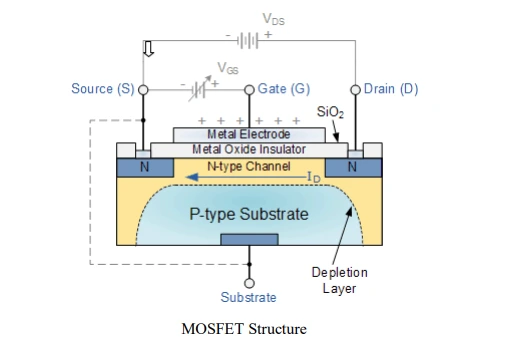
- The construction of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET is very different to that of the Junction FET. Both the Depletion and Enhancement type MOSFETs use an electrical field produced by a gate voltage to alter the flow of charge carriers, electrons for n-channel or holes for P-channel, through the semiconductive drain-source channel. The gate electrode is placed on top of a very thin insulating layer and there are a pair of small n-type regions just under the drain and source electrodes.
- Figure represents the MOSFET structure. The gate of a junction field effect transistor, JFET must be biased in such a way as to reverse-bias the pn-junction.
- With a insulated gate MOSFET device no such limitations apply so it is possible to bias the gate of a MOSFET in either polarity, positive (+ve) or negative (-ve).
- This makes the MOSFET device especially valuable as electronic switches or to make logic gates because with no bias they are normally non-conducting and this high gate input resistance means that very little or no control current is needed as MOSFETs are voltage controlled devices.
MOSFET Enhancement Type

The more common Enhancement-mode MOSFET or eMOSFET, is the reverse of the depletion-mode type. Here the conducting channel is lightly doped or even undoped making it non-conductive. This results in the device being normally “OFF” (non-conducting) when the gate bias voltage, VGS is equal to zero. The circuit symbol shown above for an enhancement MOS transistor uses a broken channel line to signify a normally open non-conducting channel.
How the MOSFET works in Enhanced Mode?
- For the n-channel enhancement MOS transistor a drain current will only flow when a gate voltage (VGS) is applied to the gate terminal greater than the threshold voltage (VTH) level in which conductance takes place making it a transconductance device.
- The application of a positive (+ve) gate voltage to n-type eMOSFET attracts more electrons towards the oxide layer around the gate thereby increasing or enhancing (hence its name) the thickness of the channel allowing more current to flow. This is why this kind of transistor is called an enhancement mode device as the application of a gate voltage enhances the channel.
Operation of a MOSFET in Enhanced Mode
- Increasing this positive gate voltage will cause the channel resistance to decrease further causing an increase in the drain current, ID through the channel. In other words, for an n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET: +VGS turns the transistor “ON”, while a zero or -VGS turns the transistor “OFF”.
- Then, the enhancement-mode MOSFET is equivalent to a “normally-open” switch.The reverse is true for the p-channel enhancement MOS transistor. When VGS = 0 the device is “OFF” and the channel is open. The application of a negative (-ve) gate voltage to the p-type eMOSFET enhances the channels conductivity turning it “ON”. Then for an p-channel enhancement mode MOSFET: +VGS turns the transistor “OFF”, while -VGS turns the transistor “ON”. Enhancement-mode N-Channel MOSFET and ci
Depletion-mode MOSFET:
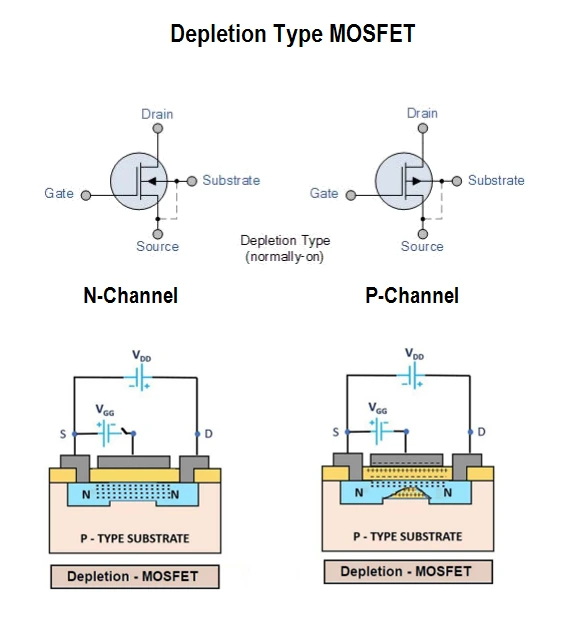
The Depletion-mode MOSFET, which is less common than the enhancement mode types is normally switched “ON” (conducting) without the application of a gate bias voltage.
How the MOSFET works in Depletion Mode?
- That is the channel conducts when VGS = 0 making it a “normally-closed” device. The circuit symbol shown above for a depletion MOS transistor uses a solid channel line to signify a normally closed conductive channel. For the n-channel depletion MOS transistor, a negative gate-source voltage, -VGS will deplete (hence its name) the conductive channel of its free electrons switching the transistor “OFF”.
- Likewise for p-channel depletion MOS transistor a positive gatesource voltage, +VGS will deplete the channel of its free holes turning it “OFF”.
- In other words, for an n-channel depletion mode MOSFET: +VGS means more electrons and more current. While a -VGS means less electrons and less current. The opposite is also true for the p-channel types. Then the depletion mode MOSFET is equivalent to a “normally-closed” switch.
MOSFET applications
- Firstly Radiofrequency applications use MOSFET amplifiers extensively.
- MOSFET behaves as a passive circuit element.
- Power MOSFETs can also be used to regulate DC motors.
- Lastly MOSFETs are used in the design of the chopper circuit.
Advantages of MOSFET
- Firstly MOSFETs operate at greater efficiency at lower voltages.
- Lastly Absence of gate current results in high input impedance producing high switching speed.
MOSFET FAQ
What is MOSFET used for?
Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistors commonly known as MOSFETs are electronic devices used to switch or amplify voltages in circuits.
What is MOSFET in simple words?
MOSFET stands for Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistors. It is a voltage controlled device and is constructed by three terminals
What are the two types of MOSFETs?
Enhanced and Depletion MOSFET. Both the p-channel and the n-channel MOSFETs are available in two basic forms, the Enhancement type and the Depletion type.
Why MOSFET is called voltage controlled device ?
MOSFET is a voltage-controlled device. By providing a positive voltage to the gate, with respect to the source, current will be made to flow in the drain.
LIKE WHAT YOU’RE READING?
CHECK OUT SOME OF OUR OTHER GREAT CONTENT HERE:
- LVDT- CONSTRUCTION, WORKING PRINCIPLE , APPLICATIONS, ADVANTAGES, AND DISADVANTAGES
- HOW AN IGBT WORKS?
- SCR VI CHARACTERISTICS EXPLAINED IN DETAIL
- STEP UP TRANSFORMER: DEFINITION, CONSTRUCTION, WORKING & APPLICATIONS
- LIMITATIONS OF OHM’S LAW
- INDUCTION MOTOR: WORKING PRINCIPLE, TYPES & APPLICATION
- STRAIN GAUGE WORKING PRINCIPLE
- WHAT IS THE ZENER DIODE? – EXPLAINED
- WHAT IS OPERATING SYSTEM AND ITS TYPE
- WHAT ARE THE USES OF CAPACITOR
- POWER FACTOR IMPROVEMENT METHODS
- WORKING PRINCIPLE OF SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR
- SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR STARTING METHOD
- WHY THE SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR IS NOT SELF STARTING



4 Comments