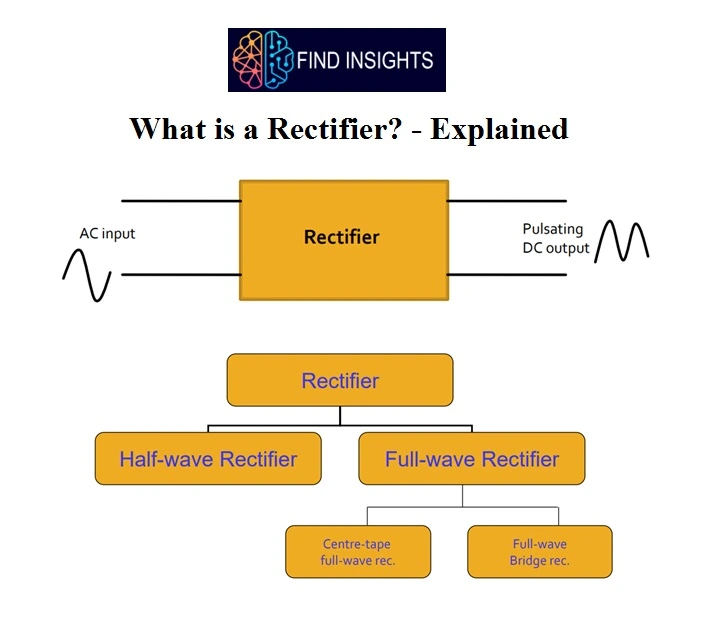
What is a Rectifier?
The process by which an alternating current (or voltage) is transformed into a direct current (or voltage) is called rectification. The device which converts alternating current (or voltage) into direct current (or voltage) is called a rectifier. Rectifiers may be made of solid state diodes, vacuum tube diodes, mercury arc valves, and also other components. Before the development of silicon semiconductor rectifiers, vacuum tube diodes and copper oxide or selenium rectifier stacks were used.
It converts the AC voltage to pulsating DC, which is smoothened by filter circuit. The output voltage of the power supply is expected remain constant against variations in the load current or variations in input voltage.
Classification of Rectifiers
- Half – Wave Rectifier
- Full – Wave Rectifier
- Bridge Rectifier
What is the Half Wave Rectifier?
- It uses a diode in series with a load resistance.
- The diode is conducting i.e. it is forward biased only for the positive half cycle of the input signal.
- Thus it provides output for only one half cycle of the input signal.
- For the other half cycle of the input the diode is reversed biased i.e. open -circuited and thus zero output is provided.
Circuit of Half Wave Rectifier

The diagram shows the Circuit of Half Wave along with Waveform.
What is a full wave Rectifier?
- This center-tap type uses only two diodes but a center-tapped (CT) transformer to establish the input signal across each section of the transformer.
- During the positive half cycle of the input, applied to the primary of transformer D1 will be forward biased assuming short-circuit equivalent and D2 will be reversed biased assuming open circuit equivalent.
- Its advantage over half wave is that it provides output for both the positive and negative half cycles.
Circuit of Full Wave Rectifier

The diagram shows the Circuit of Full Wave along with Waveform.
LIKE WHAT YOU’RE READING?
CHECK OUT SOME OF OUR OTHER GREAT CONTENT HERE:
- APPLICATIONS OF A TRANSISTOR – BJT,UJT & FET
- LVDT- CONSTRUCTION, WORKING PRINCIPLE , APPLICATIONS, ADVANTAGES, AND DISADVANTAGES
- HOW AN IGBT WORKS?
- HOW THE MOSFET WORKS?
- SCR VI CHARACTERISTICS EXPLAINED IN DETAIL
- WHAT IS THE ZENER DIODE? – EXPLAINED
- WHAT ARE THE USES OF CAPACITOR
- VARIOUS USES OF A RESISTOR
- HOW THE TRANSISTOR WORKS? – EXPLAINED



4 Comments